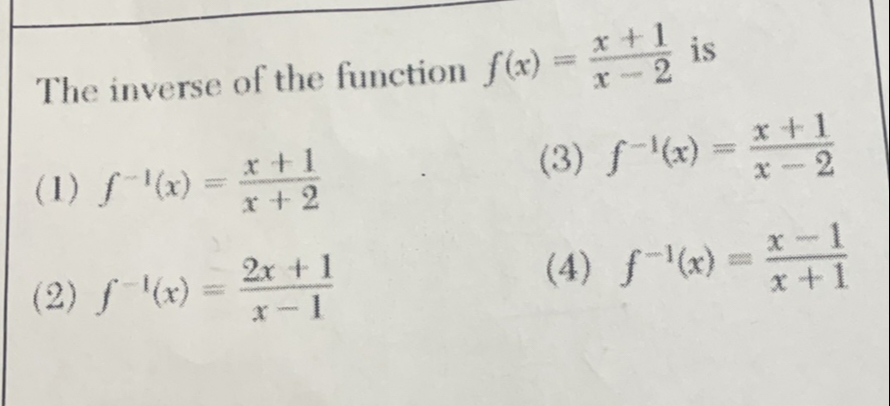AI tutor
Full solution
Q. The inverse of the function is() () () ()
- Replace with y: To find the inverse of the function , we need to switch the roles of and in the equation and then solve for . Let's start by replacing with :
- Interchange and : Now, interchange and to find the inverse function:
- Multiply by : Next, we need to solve for . To do this, we'll multiply both sides of the equation by to get rid of the fraction:
- Distribute : Distribute on the left side of the equation:
- Isolate y: To isolate y, we need to get all the terms with y on one side and the constants on the other. Let's move the y term from the right to the left side by subtracting y from both sides:
- Factor out : Factor out from the left side of the equation:
- Divide by : Now, divide both sides by to solve for :
- Inverse function found: We have found the inverse function, which is:
More problems from Multiplication with rational exponents
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help