Full solution
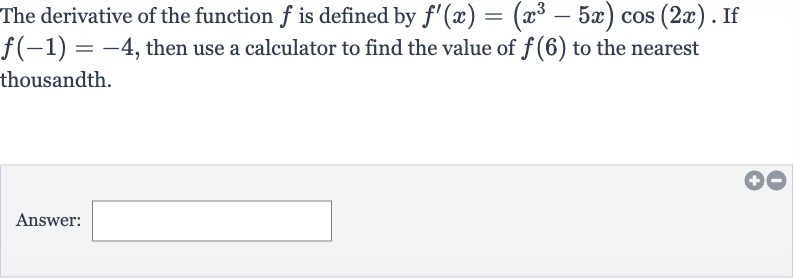
Q. The derivative of the function is defined by . If , then use a calculator to find the value of to the nearest thousandth.Answer:
- Integrate : To find , we need to integrate from to and add the result to .
- Apply integration by parts: The integral of is . We will use integration by parts and trigonometric identities to solve this.
- Integrate : Let , then . Let , then using the integral of cosine.
- Apply integration by parts again: Using integration by parts, . We apply this to our integral: .
- Integrate : We now need to integrate . This requires another integration by parts.
- Combine all parts of the integral: Let , then . Let , then using the integral of sine.
- Evaluate the definite integral: Applying integration by parts again, we get .
- Calculate : The remaining integral is , which simplifies to . This requires another integration by parts.
- Calculate : The remaining integral is , which simplifies to . This requires another integration by parts.Let , then . Let , then .
- Calculate : The remaining integral is , which simplifies to . This requires another integration by parts.Let , then . Let , then .Applying integration by parts, we get .
- Calculate : The remaining integral is , which simplifies to . This requires another integration by parts. Let , then . Let , then . Applying integration by parts, we get . The remaining integral is , which simplifies to . The integral of is .
- Calculate : The remaining integral is , which simplifies to . This requires another integration by parts.Let , then . Let , then .Applying integration by parts, we get .The remaining integral is , which simplifies to . The integral of is .So, . Now we combine all parts of the integral we've calculated.
- Calculate : The remaining integral is , which simplifies to . This requires another integration by parts.Let , then . Let , then .Applying integration by parts, we get .The remaining integral is , which simplifies to . The integral of is .So, . Now we combine all parts of the integral we've calculated.The integral from to of is the sum of all the parts we've integrated by parts. We need to evaluate this definite integral and add it to .
- Calculate : The remaining integral is , which simplifies to . This requires another integration by parts.Let , then . Let , then .Applying integration by parts, we get .The remaining integral is , which simplifies to . The integral of is .So, . Now we combine all parts of the integral we've calculated.The integral from to of is the sum of all the parts we've integrated by parts. We need to evaluate this definite integral and add it to .We evaluate the integral at the bounds and , subtract the lower bound evaluation from the upper bound evaluation, and add the result to .
- Calculate : The remaining integral is , which simplifies to . This requires another integration by parts.Let , then . Let , then .Applying integration by parts, we get .The remaining integral is , which simplifies to . The integral of is .So, . Now we combine all parts of the integral we've calculated.The integral from to of is the sum of all the parts we've integrated by parts. We need to evaluate this definite integral and add it to .We evaluate the integral at the bounds and , subtract the lower bound evaluation from the upper bound evaluation, and add the result to .Using a calculator to evaluate the integral at and , we find the change in over this interval. We then add this change to to find .
- Calculate : The remaining integral is , which simplifies to . This requires another integration by parts. Let , then . Let , then . Applying integration by parts, we get . The remaining integral is , which simplifies to . The integral of is . So, . Now we combine all parts of the integral we've calculated. The integral from to of is the sum of all the parts we've integrated by parts. We need to evaluate this definite integral and add it to . We evaluate the integral at the bounds and , subtract the lower bound evaluation from the upper bound evaluation, and add the result to . Using a calculator to evaluate the integral at and , we find the change in over this interval. We then add this change to to find . After calculating the definite integral and adding it to , we round the result to the nearest thousandth to get the final answer.