Full solution
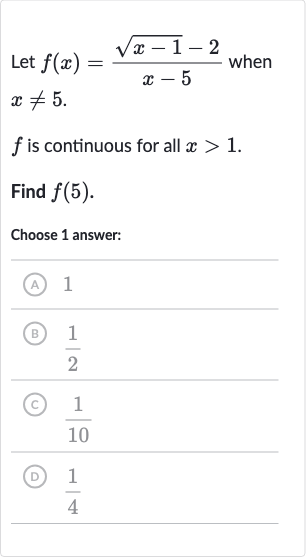
Q. Let when . is continuous for all .Find .Choose answer:(A) B) (C) (D)
- Understand the problem: Understand the problem.We need to find the value of the function at . However, the function is not defined at because it would result in a division by zero. Since the function is continuous for all x > 1, we can use the limit process to find .
- Set up the limit: Set up the limit to find . To find , we need to calculate the limit of as approaches .
- Apply L'Hôpital's Rule: Apply L'Hôpital's Rule.Since the limit is of the form , we can apply L'Hôpital's Rule, which states that if the limit of as approaches a value is or , then the limit is the same as the limit of the derivatives of and as approaches .
- Differentiate the numerator and denominator: Differentiate the numerator and denominator. derivative of derivative of Now we have:
- Calculate the limit: Calculate the limit.Now we substitute into the derivative of the numerator:
- Conclude the solution: Conclude the solution.Since the limit as approaches of is , and the function is continuous for all x > 1, we can conclude that .
More problems from Domain and range of square root functions: equations
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help