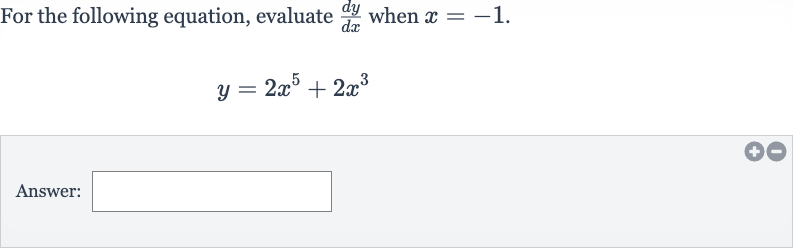Full solution
Q. For the following equation, evaluate when .Answer:
- Apply Power Rule: To find the derivative of with respect to , we need to apply the power rule of differentiation, which states that the derivative of with respect to is .
- Differentiate : Differentiate the first term using the power rule: The derivative is .
- Differentiate : Differentiate the second term using the power rule: The derivative is .
- Combine Derivatives: Combine the derivatives of both terms to get the overall derivative : .
- Substitute : Now, substitute into the derivative to evaluate at : .
- Calculate Powers: Calculate the powers of : and .
- Substitute Values: Substitute the values back into the expression: .
- Find Final Value: Add the numbers to find the value of when : .
More problems from Evaluate a function: plug in an expression
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help