AI tutor
Full solution
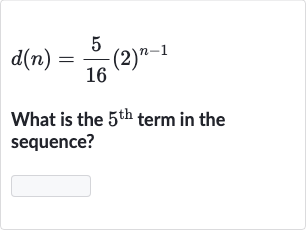
Q. What is the term in the sequence?
- Substitute : To find the term in the sequence, we need to substitute into the formula .
- Calculate the exponent: Substitute into the formula: .
- Calculate : Calculate the exponent: .
- Multiply the result: Calculate : .
- Simplify the expression: Multiply the result by : .
- Expression simplifies to: Simplify the expression: .
- Final result: Since equals , the expression simplifies to: .