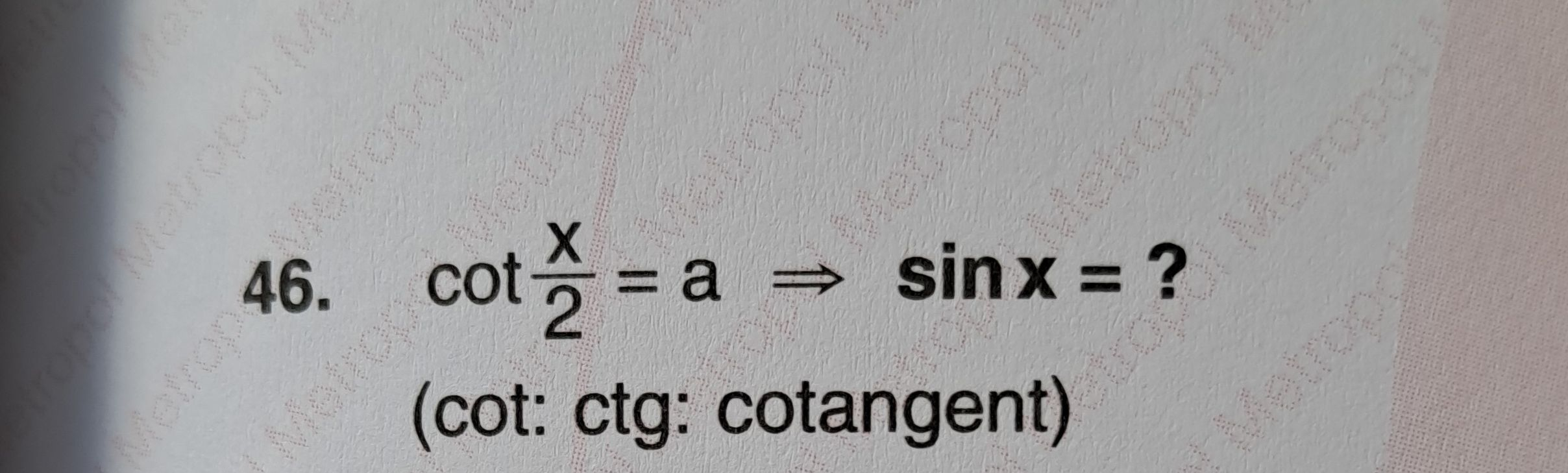AI tutor
Full solution
Q. ?(cot: ctg: cotangent)
- Express : Express in terms of sine and cosine.Cotangent is the reciprocal of tangent, which is sine over cosine. Therefore, can be written as .
- Use Pythagorean identity: Use the Pythagorean identity to express in terms of . The Pythagorean identity states that . We can solve for by rearranging the identity to and then taking the square root.
- Express : Express in terms of and using the double angle formula.The double angle formula for sine is .
- Substitute into formula: Substitute the expression for into the double angle formula.Since , we can write as .
- Simplify : Simplify the expression for . The terms cancel out, leaving us with . Since is given as , we have .
More problems from Sin, cos, and tan of special angles
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
QuestionGet tutor help
Question
. Find the value of in degrees.Write your answer in simplified, rationalized form. Do not round.____
Get tutor helpQuestionGet tutor help