Full solution
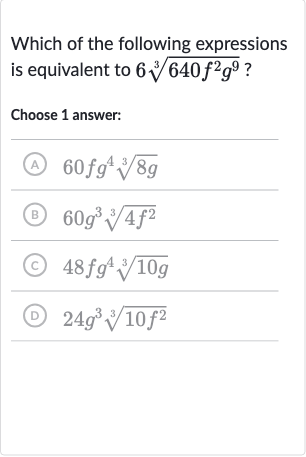
Q. Which of the following expressions is equivalent to ?Choose answer:(A) (B) (C) (D)
- Simplify Expression: First, let's simplify the expression inside the cube root. can be factored into prime factors: . The expression becomes .
- Split into Separate Roots: We can split the cube root into separate roots for each factor:
- Simplify Each Cube Root: Now, we simplify each cube root separately. For , we can take out (which is ) from the cube root because is a perfect cube. This leaves us with .
- Multiply Constants: For , is a perfect cube (since is divisible by ), so we can take out of the cube root. This gives us
- Combine Numbers Inside Root: For , we cannot simplify further since is not divisible by . So, it remains inside the cube root.
- Compare with Answer Choices: Now, we multiply the constants outside the cube root: . The expression now is .
- Compare with Answer Choices: Now, we multiply the constants outside the cube root: . The expression now is . We can combine the numbers inside the cube root: . The expression simplifies to .
- Compare with Answer Choices: Now, we multiply the constants outside the cube root: . The expression now is . We can combine the numbers inside the cube root: . The expression simplifies to . We compare the simplified expression with the answer choices. The expression matches with choice (D).
More problems from Identify equivalent linear expressions I
QuestionGet tutor help