Full solution
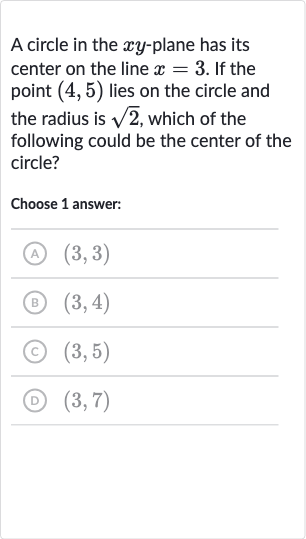
Q. A circle in the -plane has its center on the line . If the point lies on the circle and the radius is , which of the following could be the center of the circle?Choose answer:(A) (B) (C) (D)
- Circle Distance Formula: Determine the distance formula for a circle. The distance between the center of a circle and any point on the circle is equal to the radius when using the distance formula:
- Apply Formula to Given Point: Apply the distance formula using the given point and the potential centers on the line . Since the -coordinate of the center must be , we only need to find the correct -coordinate. The radius is given as .
- Check Option (A): Substitute the known values into the distance formula for each option and check if the distance equals . Start with option (A) : , which is not equal to .
- Check Option (B): Check option (B) : , which is equal to . This could be the center of the circle.
- Check Remaining Options: For completeness, check the remaining options. Option (C) : , which is not equal to . Option (D) : , which is not equal to .
- Final Answer: Therefore, the centre of the circle is .